Everything You Need To Know About Solar Inverters

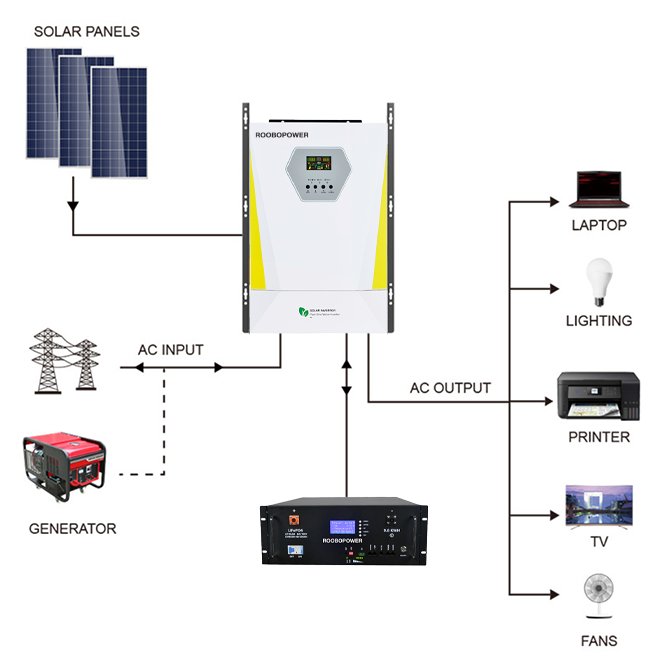
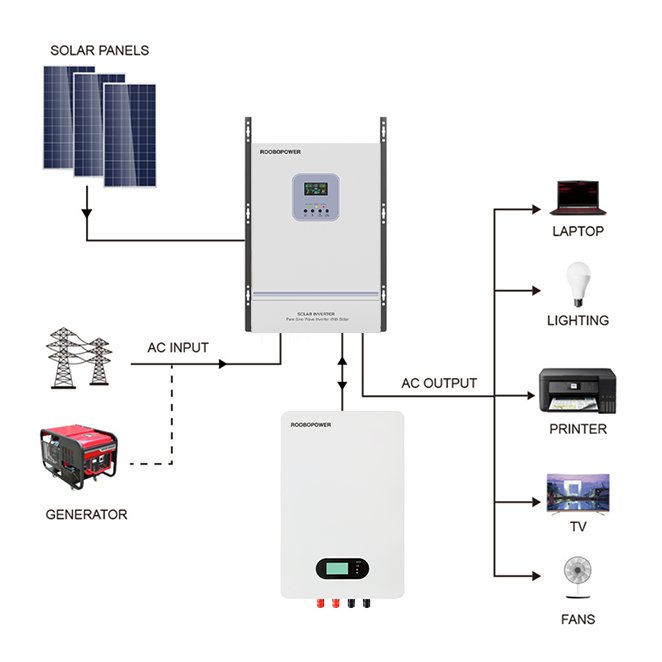
Solar inverters make powering your home with solar energy possible. Houses are wired to operate on alternating current (AC) power. Every photovoltaic solar energy system for use with household electricity requires a way to transform the direct current (DC) energy created by the solar panels to AC power. The power inverter your home’s solar energy array requires will depend on several factors.
What Is a Solar Inverter?
Solar inverters’ main function is to accept DC power input and turn it into AC power. They also act as the primary connection between the panels and the electrical distribution panel in the house. Modern inverters contain switches that can connect or isolate your solar energy system from the power grid and provide detailed information to your system’s monitoring equipment.
A solar inverter isn’t a charge controller. A charge controller manages electrical input and distributes it to batteries or the electrical system. They’re integral to solar energy storage systems in addition to inverters.
How a Solar Inverter Works
A solar inverter is essential for your solar panel system to convert DC electricity into AC electricity for everyday use. It’s also a critical part of your system; understanding how it works is important to get the most out of your solar panels.
The process begins with sunlight striking the photovoltaic cells of solar panels, creating a flow of DC electricity. However, since most homes and electrical grids use AC electricity, the DC electricity generated by solar panels needs to be converted. This is where the solar inverter steps in. Its main task is to convert the DC electricity into AC electricity with the appropriate voltage, frequency and phase, making it suitable for powering household appliances and feeding excess energy into the electrical grid.
Why Is It Called an Inverter?
Early household electric appliances ran on DC instead of AC. Up-and-coming large power generators were starting to produce AC energy more efficiently than DC. A converter was necessary to change the AC power from the power plant to usable DC energy.
As time passed, appliances gradually switched from using DC to AC. It was discovered that the device would produce the opposite effect and change DC power to AC by inverting the wire connections on a converter. Thus, the inverter was born. Modern inverter versions are used today in solar energy production.
Types of Solar Inverters
There are two types of solar inverters. One of which can be enhanced to perform more efficiently. Although they perform similar functions, the main difference is when they do it instead of how. That difference means each type works best under different circumstances.
String Inverter
A string inverter, or central inverter, is a large device that accepts DC input from multiple solar panels and transforms all of the energy to AC. You could say that it works to transform energy in bulk amounts.
In a solar energy system with a string inverter, all or several solar panels are wired into one centrally located inverter. The inverter then feeds the electrical panel or the grid. In short, a string inverter changes the power from DC to AC after the power is collected from the solar array.
Microinverter
You’ll need more than one microinverter. Microinverters are located at each solar panel and convert that panel’s energy immediately before sending it to the house electrical to meet up with all of the other inverters’ power.
A solar energy system that uses microinverters treats each solar panel as its own
AC power source and feeds the energy to the home or electrical grid.
String Inverter With Optimizers
Technically not a different type of inverter; a string power inverter with optimizers is a combination of components. In such a system, a solar panel has an optimizer that gathers as much DC power as the panel can generate and sends it to the central inverter. The other optimizers do the same. The inverter collects the DC energy from each optimizer and inverts it into AC as a whole before sending it to the house or grid.
Pros and Cons
The best solar inverter for your home depends on the conditions surrounding your system.
String Inverter
String inverters are excellent for use in solar energy systems where all panels face the same direction on one plane that experiences little disruption from shade or other sun-blocking elements.
Pros
String inverters are the least expensive inverter option. They are simple to install and wire and have fewer components that can break. Maintenance is easy, and troubleshooting or repair work is simplified by all elements being in one location.
Cons
String inverters can’t discern which panel is sending power. Because all of the panels send energy to the inverter in bulk, if one panel stops or slows production, the entire system becomes limited to the maximum power generation of the weakest panel. In other words, the whole system is less productive if one panel experiences less sunshine than the others due to shade, snow cover or other elements.
Also, string inverters handle a lot of power simultaneously, which generates heat. The heat must be dissipated by placing the unit in the shade, cooling it with fans or both to keep it running efficiently.
Microinverter
Microinverters are great for use in solar energy systems where not all panels face the same direction or parts of the array experience shade for some of the day. They also work well for those who may enlarge their system later due to their expandability.
Pros
Microinverters immediately change the DC power to AC at the solar panel. If one panel or inverter slows production or fails, the other panels and microinverters aren’t affected, and each one can continue to provide maximum power to the system.
Microinverters are small devices that don’t generate much heat and don’t require mechanical cooling to maintain optimal energy efficiency. For that reason, they also last longer than string inverters.
Cons
Microinverter technology is more expensive than string inverter technology, and each panel requires its own inverter, so you must purchase more units. That means that the system as a whole is more costly than its counterpart.
In addition, there are more active components in a microinverter system, and those parts are located on the roof. Meaning maintenance is more involved, and troubleshooting or repairs are more expensive.
String Inverter With Optimizers
A string inverter with a power optimizer system is the best of both worlds for some consumers.
Pros
Power optimizers act similarly to micro inverters in that each panel is independent of the next. That means that shade or sun-blocking on one panel doesn’t affect the efficiency of others or the system in general.
Additionally, power optimizers can monitor each panel’s output for easy troubleshooting. The associated string converter has fewer active components than a microinverter system and is easy to maintain and repair.
Cons
String inverters with optimizers are more expensive than a simple string inverter system. Also, the optimizers are located on the roof at each solar panel, so repairing parts of the system can be more costly.
Cost of a Solar Inverter
The cost of a solar inverter is one of the most important factors in determining whether or not your solar power system will be cost-effective. Luckily, a high-quality solar inverter is now possible at a reasonable price.
If you’re looking to install a solar energy system, knowing the cost of a solar inverter is essential to figure out your total solar cost. Residential solar inverters typically range from $1,000 to $2,000, with string inverters being the more affordable option. String inverters are centralized devices that convert the combined DC output of multiple solar panels into AC electricity, offering a cost-effective solution for residential and small commercial solar installations.
Microinverters are individual devices attached to each solar panel, optimizing their performance and enabling greater energy yield, especially in scenarios with partial shading or different panel orientations. They are much more expensive than string inverters and can cost $1,000 or more.
Power optimizers are electronic devices installed on each solar panel, working in tandem with a central inverter to maximize energy production by managing the output of individual panels and mitigating the effects of shading or mismatched panel configurations. However, power optimizers can be pricier, offering individual panel optimization, costing between $50 to $200 per panel.
The overall cost of a solar inverter installation also includes additional expenses such as installation fees, required accessories such as wiring or conduit pipes and potential government incentives or subsidies, which can vary based on location and the project’s complexity.
How Long Does a Solar Inverter Last?
When planning your solar energy system, it’s important to consider the expected how long the solar inverter will last. Although the lifespan of a solar inverter is typically between 10 and 15 years, factors like proper maintenance and care, good ventilation and operating conditions can contribute to a longer lifespan. Ultimately, considering the expected lifespan of a solar inverter is essential when planning the long-term benefits of a solar energy system.
How to Choose a Solar Inverter
There are several variables to consider when choosing how to transform the power from your solar energy system into usable electricity. To make a solar panel system worth the investment, you’ll want to install the most efficient components at a reasonable price.
Microinverter systems are the most expensive type of inverters. However, they last longer than string inverters and are more reliable overall. Expect warranties and lifespans of microinverters to range from 15 to 25 years, while string inverters are warranted for an average of 10 years.
The most efficient system for your home depends mainly on the panel location and shade patterns on your property. In general, the most efficient system for unshaded solar panels on a single plane will employ a string inverter. Microinverter or optimizer systems are best for shady areas or panel systems that aren’t continuous.
What Size Solar Inverter Do I Need?
Choosing the right solar inverter size is one of the most important decisions you’ll make when building a solar energy system. Improperly sizing your inverter can lead to inefficiencies in your system, resulting in higher electricity bills and even damage to your property.
The best way to ensure you choose the right solar inverter size is by following this simple rule: select an inverter with a greater capacity than your total solar panel capacity. Inverters tend to have efficiency losses during the DC to AC-conversion process, which means they will produce less AC power than they are typically rated for.
When sizing your inverter, you should also consider your household’s power consumption patterns and peak power demand. For instance, suppose you have high peak loads due to heavy appliances such as air conditioners or electric heaters. In that case, your inverter must handle those loads without being significantly overworked.